PART
1
Coffee
has become daily needs for majority of people. Almost every day, people consume
coffee for breakfast, lunch and even dinner. And nowadays, coffee is not only
popular among adult people but also young or teenager. Related to article,
there are some problem caused by global warming such as drastic climate change
and another problem is low price that are discouraging farmers from increasing
output. From the news taken from New York, to avoid a shortage of coffee, world
needs another Brazil as top grower and exporter of coffee. In the next decade,
global production will raise from 40 billion to 50 billion because of threat of
climate change and following by low price that are discouraging farmer from
increasing output. The world set coffee production deficit of 3.5 million bags
in 2015-2016 and that follows a global shortage of 6.4 million bags per year.
Since 2015, price has retreated 27 per cent as Brazil currency against dollar.
Production coffee at 2014 has pegged at 144 billion this year and may rise to
meet consumption for a balance market in 2030 as long as smallholder’s farmer
can boost the productivity. Climate change threatens in quarter Brazil’s output
in Nicaragua, El Salvador and Mexico are facing potential losses unless farmers
adapt. According to report, producing probably shift from Central America to
the Asia-Pacific region or eastern parts of Africa, where crops can be grown at
higher altitudes. Arabica coffee, the premium bean that was used by shops
including Starbucks Corp., is most at risk from rising temperatures and illy
uses only Arabica. Brazil is the largest Arabica grower and Vietnam is the
biggest producer for Robusta.
MARKET
EQUILIBRIUM- DEMAND AND SUPPLY
The
curve that shows relationship between price of product and quantity of product
supplied it is called supply curve. In supply curve, there is a law of supply.
Law of supply means that holding everything else constant “ceteris paribus” and
it has positive relationship, means when price go down, quantity demanded will
decrease and when the price go up, quantity demanded will increase. There are
two factor influences market demand related to the article, which is climate
change and low price. Climate change in Brazil makes production coffee
decrease. Besides climate change in Brazil, the other factor is low price. Low
price make farmers unwilling to produce more coffee. Market equilibrium is the
situation when quantity demanded equal to quantity supplied. The graph shows
that the curve shift to the left because of production of coffee in Brazil is
decrease.
This
graph shows change in supply shift to the left because of decrease in supply.
This graph also shows change in equilibrium, because of supply shift to the
left from S1 to S2. Equilibrium quantity of products decrease from Q1 to Q2 and
the equilibrium price increase from P1 to P2. This graph explains change in
supply. Because of climate change and low price in coffee production that make
farmer unwilling to produce more, supply of coffee decrease. Therefore in the
supply curve shifts to left, indicating decreasing of supply.
On
the other side which is related to the article, global coffee consumption will
increase by a third to 200 million in 2030. It means that on 2030 demand of
coffee consumption will increase. The definition of demand curve is the curve
that shows the relationship between the price of product and the product
demanded. Law of demand has negative relationship means that when price go up
quantity demanded will decrease and when price go down the quantity demanded
will increase.
The graph shows that there is an increase in demand, demand shift to the right from D1 to D2. Equilibrium price rises from P1 to P2 and equilibrium quantity rises from Q1 to Q2. This graph explains increase in coffee demand because related to article demand will increase to 200 million bags in 2030.Therefore the demand curve shift to the right.
CONSUMER
SURPLUS, PRODUCER SURPLUS AND DEADWEIGHT LOSS
The
difference between highest price a consumer willing to pay for goods or service
and actual price the consumer receives called consumer surplus. Producer
surplus means the difference between lowest price a firm would be willing to
accept for a good or service and the price it actually receives. If the
quantity of coffee in Brazil is too low, the value to consumer of the next unit
exceeds the cost to producers. That is the reason why world needs another
Brazil to avoid shortage.
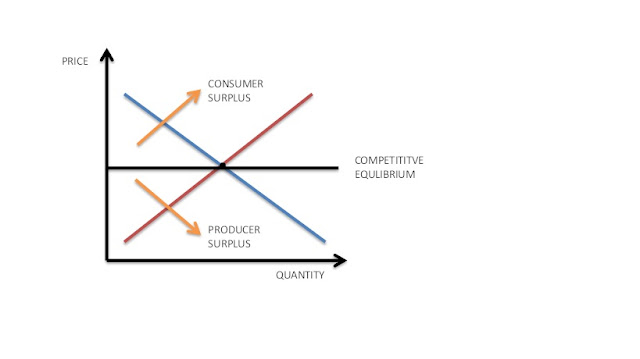 First
graph shows consumer surplus on A and producer surplus on B. This is reach
economic efficiency when Marginal Benefit equals to Marginal Cost and sum of
consumer and producer surplus is maxed. Marginal Benefit is additional cost to
a firm of producing one more unit of goods or service or we can also say
marginal benefit is additional satisfaction that person receive for consuming
additional goods or services. This graph shows before shortage appears.
First
graph shows consumer surplus on A and producer surplus on B. This is reach
economic efficiency when Marginal Benefit equals to Marginal Cost and sum of
consumer and producer surplus is maxed. Marginal Benefit is additional cost to
a firm of producing one more unit of goods or service or we can also say
marginal benefit is additional satisfaction that person receive for consuming
additional goods or services. This graph shows before shortage appears.
Second
graph shows after shortage appears. The consumer surplus changes from D and C
to D and B. This graph still related to first graph where we can see there is a
shortage. Because there is a shortage, producer surplus decline from A, B and E
to A and there are deadweight loss on C and E. This shortage will happen
because of rising on demand and the production drop because of climate change. Price
floor is minimum price that sellers can receive. Because of this shortage and
price ceiling, producers have to reduce their price.
MARKET
STRUCTURE
There
are several types for market structure which are perfectly competitive market,
monopoly, monopolistically competitive and oligopolies. Based on several
articles that I read, Brazil actually not only the only one that produce Arabica,
but Brazil is the biggest exporter of Robusta. That is why coffee-drinking
world are very rely on Brazil coffee production. But, Brazil categorized
oligopoly on market structure. Oligopoly means a market structure with a small
number of independent firms compete. Oligopolies characteristic are, there are few
numbers of firms or countries, means that only several firms or country that
produce coffee. In this case countries that produce Arabica coffee besides
Brazil are Vietnam, India, Indonesia, Uganda and Malaysia. Another
characteristic are the type of product is identical or differentiated and low
ease of entry. The meaning of low ease of entry is that it is quite hard to
another firms or country if they want to entry to the market competition
because there are only several firms or country inside and need a large
resource to compete with another country. And another characteristic of
oligopoly is producer become price taker. It means that they can control the
price and all decision that countries do will affect market.
PART
3
After
all brief explanation about climate change in Brazil that can make rising
demand and coffee shortage, we can see that demand of coffee will be increasing
in 2030. That is why coffee production will have to rise about 40 million to 50
million in the next decade. But there is a problem because of climate change
and low price that make farmers unwilling to produce more. Therefore we can
conclude that the demand increases and the supply decreases. If there is a
shortage, the producer surplus will decrease means that the producer must
decrease their price. Consumer surplus
become larger but producer cannot fulfil demand from consumer and the
deadweight loss also come up. That is why to avoid shortage, people needs
another Brazil to supply coffee needs. For all this time, Brazil became one of
the biggest Arabica growers and Vietnam became the biggest producer of Arabica
coffee. Related to article and another article that I read before, Brazil is
not the one that produces Arabica coffee. There are several countries that
produce Arabica coffee. Therefore I can conclude that Brazil is Oligopoly. From
this issue, I can suggest that producing area may move to another country like Asia-Pacific
region or may move to eastern part of Africa. Therefore coffee production not
always relies on Brazil production but also we can get coffee production for
another country.
Reference lists :
Hubbard, R.G. and O’Brien, A.P. (2015). Economics.England :Pearson Education Learning.
The star .(2015). Climate change, rising demand could mean coffee shortage.[online]. Available
from : http://www.thestar.com/business/2015/10/01/climate-change-rising-demand-could-mean-coffee-shortage.html
[ accessed 21 October 2015]
Index mundi (2015). Green Coffee Robusta Production by Country in 1000 60 KG BAGS [online].
Available from: http://www.indexmundi.com/agriculture/?commodity=green-coffee&graph=robusta-production
[Accessed 26 October 2015]


